Hello Friends, Today I am Telling you About Topology ?
NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
In a point-to-point link, two devices monopolize a communication medium.
Because the medium is not shared, a mechanism is not needed to identify the computers.
1. Simplex
NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
- Understand what Topology is.
- Understand different Topologies.
- Two computers communicating via modems.
- A workstation communicating along a parallel cable to a printer.
In a point-to-point link, two devices monopolize a communication medium.
Because the medium is not shared, a mechanism is not needed to identify the computers.
Therefore, a simple,two-device point-to-point network has no need for addressing.
Point-to-point links can be simplex, half-duplex, or full-duplex.
When devices must engage in bi-directional communication on a half-duplex link,
some turn around mechanisms must be in place to switch the roles of the sending and receiving devices.
1. Simplex
- Signal flows in ONE direction.
- Only one station transmit and the other receive.
- Each station can both transmit and receive but NOT at the same time.
- Both stations transmit and receive simultaneously
- Link capacity is shared between the two devices either by 2 separate transmission path.
- Channel capacity is divided for transmitting and receiving.
- Link three or more devices together through a single communication medium
- For sharing a common channel, each device needs a way to identify itself and the device to
which it wants to send information. The method used to identify senders and receivers is called addressing.
Three common types of multi-point topology:
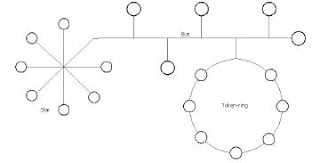
- Bus
- Ring
- Star
Sharing of channel’s capacity
1. Spatial sharing – all attached devices using the link simultaneously 2. Time sharing – devices take turn in using the link Bus Devices connected to a single linear cable called a trunk
1. Spatial sharing – all attached devices using the link simultaneously 2. Time sharing – devices take turn in using the link Bus Devices connected to a single linear cable called a trunk
• Bus consists of a single linear cable called a trunk.
• Data is sent to all computers on the trunk. Each computer examines EVERY
packet on the wire to determine who the packet is for and accepts only
messages addressed to them.
• Bus is a passive topology.
• Performance degrades as more computers are added to the bus.
• Signal bounce is eliminated by a terminator at each end of the bus.
• Barrel connectors can be used to lengthen cable.
• Repeaters can be used to regenerate signals.
• Usually uses Thinnet or Thicknet
• both of these require 50 ohm terminator
• good for a temporary, small (fewer than 10 people) network
• But its difficult to isolate malfunctions and if the backbone goes down, the
entire network goes down
• Terminators should be applied to both ends of the longest path
• Nodes connected to the bus cable by drop lines and taps
1. Drop lines – connection between a node and the main cable
2. Taps – connector either splices into the main cable or punctures the sheathing of a cable to
create a contact with the metallic core Advantages:
create a contact with the metallic core Advantages:
- Easy to use and understand
- Less number of cable required
- Inexpensive simple network
- Easy to extend a network by adding cable with a repeater that boosts the signal
and allows it to travel a longer distanceDisadvantages:
- Becomes slow by heavy network traffic with a lot of device because network do not
coordinate with each other to reserve times to transmit.
- Difficult to Troubleshoot a bus because a cable break or loose connector will cause
reflections and bring down the whole network.
- Computers are connected on a single circle of cable.
- Usually seen in a Token Ring or FDDI (fiber optic) network.
- Each computer acts as a repeater and keeps the signal strong => no need for repeaters on a
ring topology.
- No termination required => because its a ring.
- Token passing is used in Token Ring networks.
- The token is passed from one computer to the next, only the computer with the token can transmit.
- The receiving computer strips the data from the token and sends the token back to the sending computer with an acknowledgement.
- After verification, the token is regenerated.
- Relatively easy to install, requiring ;minimal hardware.
- One device cannot monopolize the network.
- Continue to function after capacity is exceeded but the speed will be slow.
- Failure of one device can affect the whole network.
- Difficult to Troubleshoot.
- Adding and removing devices distrupts the network.
- Computers are connected by cable segments to a centralized hub.
- Signal travels through the hub to all other computers.
- Requires more cable.
- If hub goes down, entire network goes down.
- If a computer goes down, the network functions normally.
- Most scalable and reconfigurable of all topologies.
- The failure of a single device or cable doesn't bring bring down the entire network.
- The Centralized networking equipment can reduce costs in the long run by making
network management much easier.
- It allows several cable types in same network with hub.
- The can accommodate multiple cable types.
- Failure of the central device (HUB) causes the whole network failure.
- It is slightly more expensive than using bus topology.
- Often mirrors corporate structure.
- Use Polling.
- One fails, others can function independently.
Advantages:
- Combine the benefits of several different types of topologies.
- Workgroup efficiency and traffic can be customized.
- Devices on one topology cannot be placed into another topology without some hardware changes
Like Hybrid Topology but no additional hardware required for changing data packet between topologies
LonWorks uses this type of topology
Advantages:
- Very easy to install.






No comments:
Post a Comment